|
Email / CV / LinkedIn / Google Scholar / GitHub |

|
|
I am an Assistant Professor in the Department of Artificial Intelligence at University of Seoul (starting March 2026), where I research more human-like, real-time voice and omni-modal agents. Previously, I was a Senior Research Engineer at Qualcomm AI Research Korea (until February 2026). I received my Ph.D. as a candidate at the Data Science & AI Lab (DSAIL) at Seoul National University (SNU). My research there primarily focused on speech synthesis (text-to-speech, voice conversion) and speech large language and dialog models (speech LLMs), and I also explored generative models in other domains (vision, NLP, ...). I received my B.S. in Electrical and Computer Engineering from Seoul National University. |
|
|
I have a broad interest in generative models, and I am currently particularly focused on multimodal large language models in speech and audio. Specifically, I am interested in speech large language models (speech LLMs) and spoken dialog models. Additionally, both now and in the past, I have conducted research with a focus on diffusion models. My previous research primarily centered around speech synthesis, where I worked on tasks such as text-to-speech and voice conversion, with a focus on keywords like personalization and data efficiency. Below are my representative works.
|
|
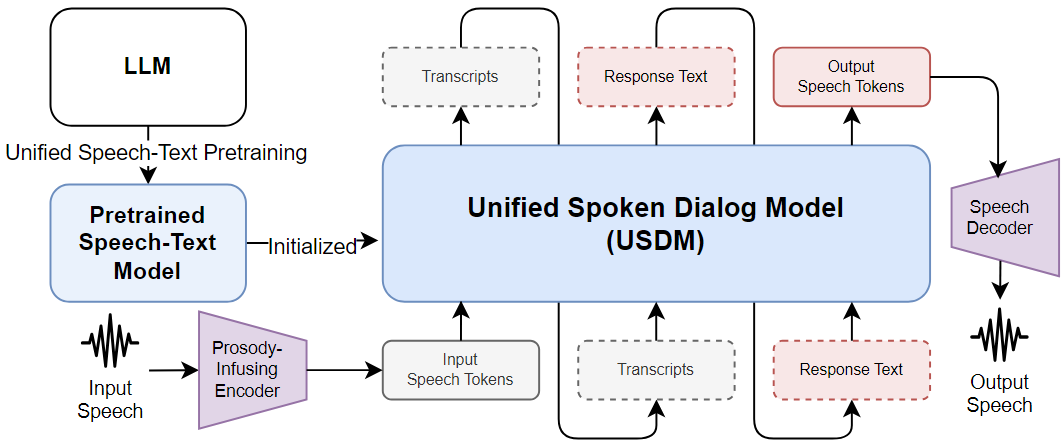
During my time at DSAIL, I collaborated with NAVER Cloud on developing spoken language and spoken dialog models based on pre-trained large language models (LLMs). In this project, we extended a pre-trained LLM into a spoken language model by leveraging a large-scale speech-text paired dataset and further expanded it into a spoken dialog model through supervised fine-tuning. I successfully built a USDM, an English end-to-end spoken dialog model that incorporates paralinguistic features and contributed to the construction of Naver’s end-to-end Korean spoken dialog model, SpeechX. Project Overview
Related Articles & Blog Posts
|
|
|

|
Electrical and Computer Engineering Mar 2019 - Aug 2025 Electrical and Computer Engineering Mar 2015 - Feb 2019 |
|
|
|
Below is a list of my publications. |
|
Heeseung Kim, Soonshin Seo, Kyeongseok Jeong, Ohsung Kwon, Soyoon Kim, Jungwhan Kim, Jaehong Lee, Eunwoo Song, Myungwoo Oh, Jung-Woo Ha, Sungroh Yoon, Kang Min Yoo Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2024 arXiv / code / demo USDM is a paralinguistic-aware spoken dialog model built through supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on spoken dialog data, on top of a cross-modal pretrained model trained using a speech-text interleaving technique. |
|
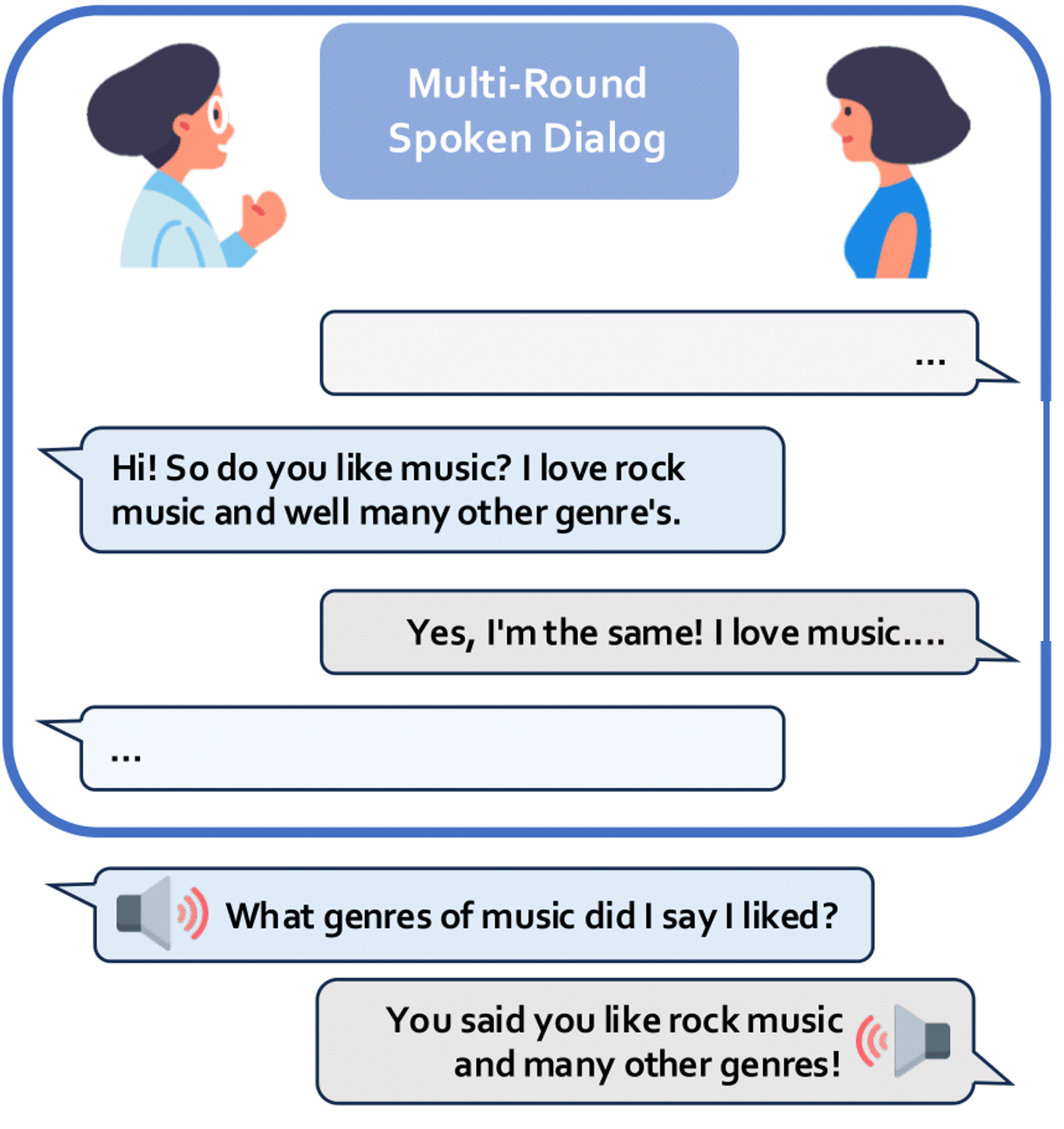
Heeseung Kim*, Che Hyun Lee*, Sangkwon Park, Jiheum Yeom, Nohil Park, Sangwon Yu, Sungroh Yoon ACL Findings, 2025 arXiv / demo / dataset We propose ContextDialog, a benchmark to evaluate a model’s ability to utilize past information, and observe and analyze that open-source multi-turn voice interaction models often fail to recall past information and, even in RAG scenarios, remain highly error-prone, resulting in inadequate responses. |
|
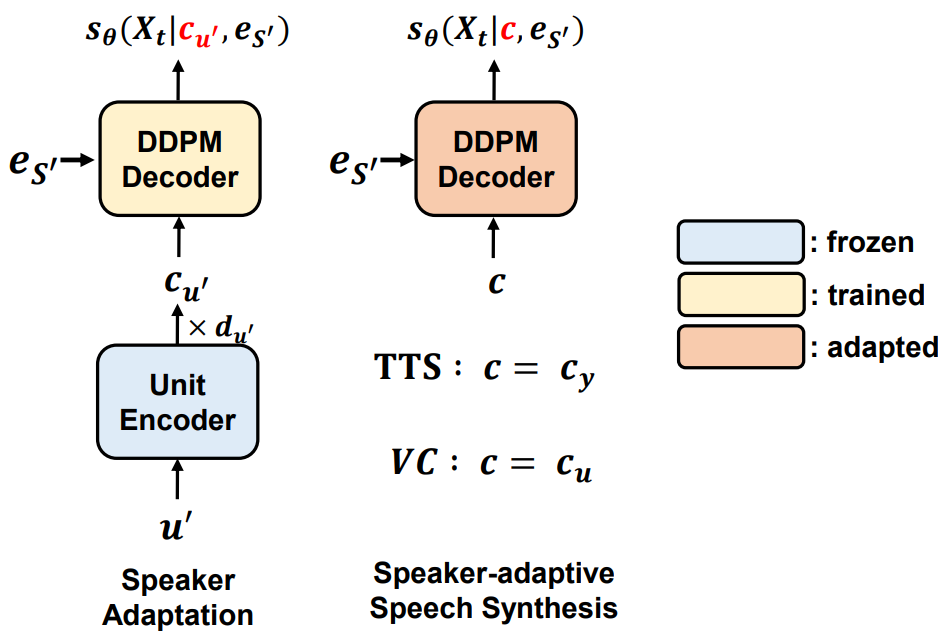
Heeseung Kim, Sungwon Kim, Jiheum Yeom, Sungroh Yoon INTERSPEECH, Oral Presentation, 2023 arXiv / code / demo UnitSpeech is a speaker adaptation model that enables personalized text-to-speech and any-to-any voice conversion with only 5 to 10 seconds of untranscribed speech. |
|
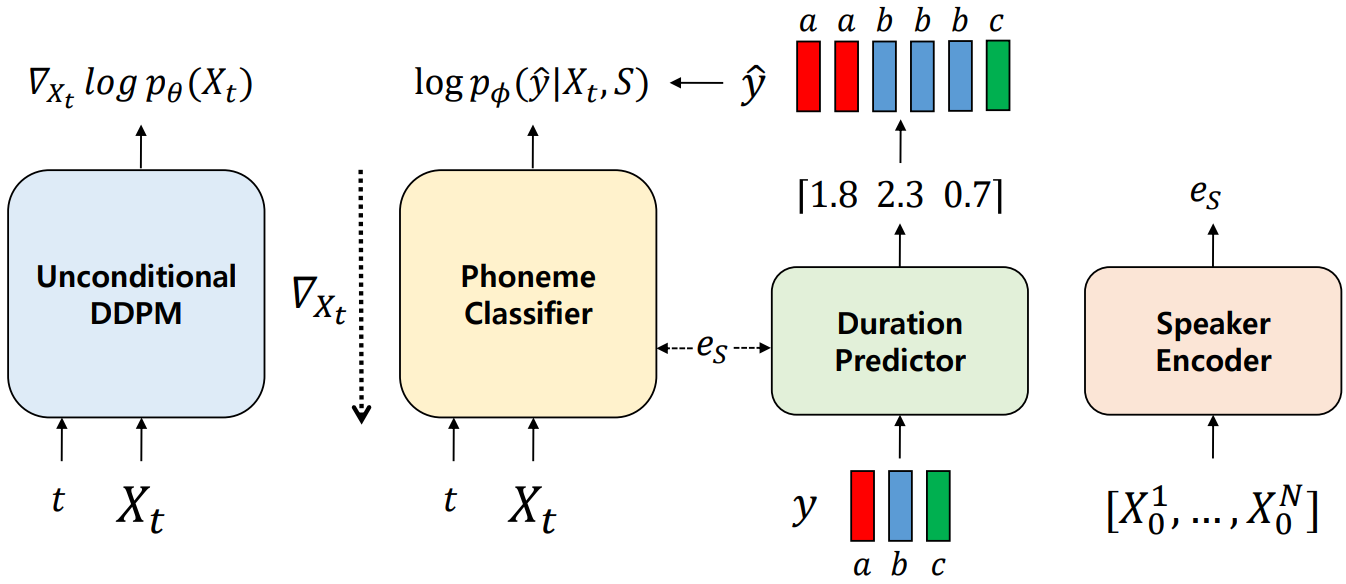
Heeseung Kim*, Sungwon Kim*, Sungroh Yoon International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2022 arXiv / demo Guided-TTS is a method for building a TTS model using long-form untranscribed speech data of the target speaker. |
|
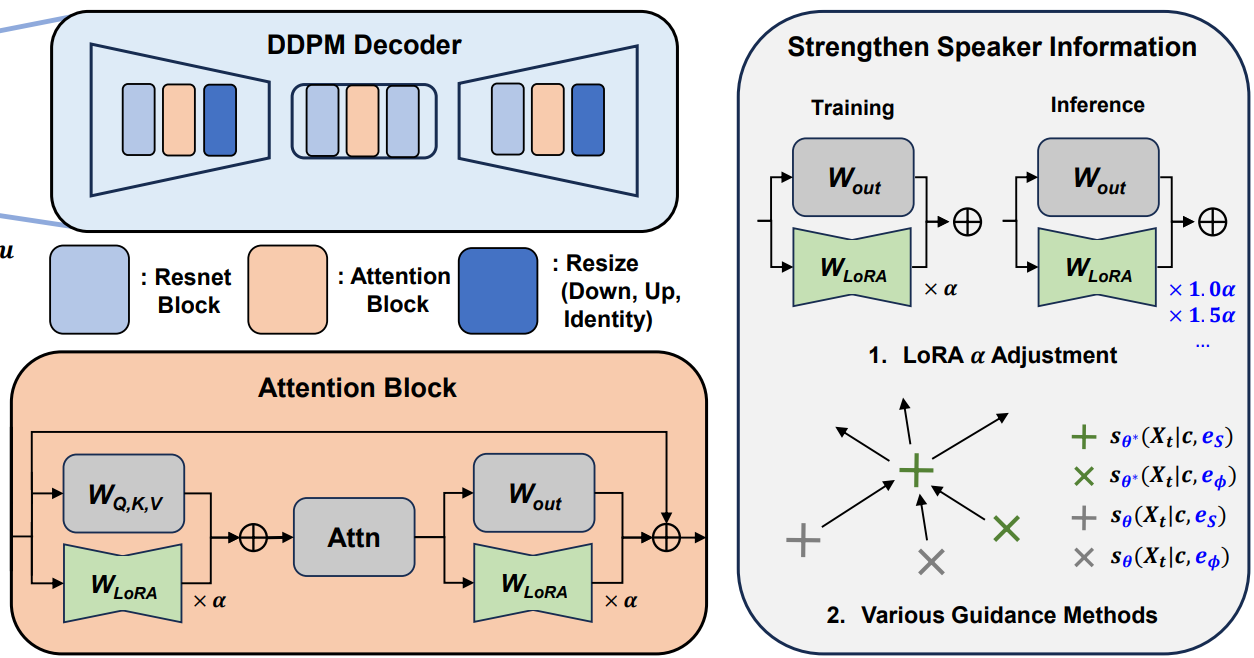
Heeseung Kim, Sang-gil Lee, Jiheum Yeom, Che Hyun Lee, Sungwon Kim, Sungroh Yoon INTERSPEECH, 2024 project page / arXiv VoiceTailor is a one-shot speaker-adaptive text-to-speech model, which proposes combining low-rank adapters to perform speaker adaptation in a parameter-efficient manner. |
|
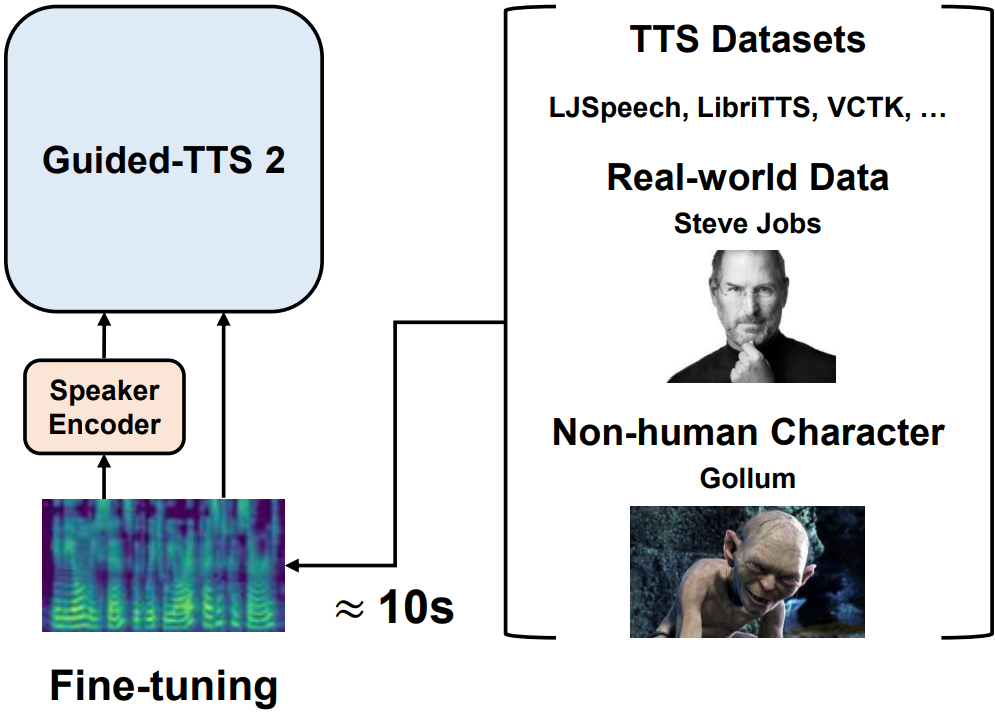
Sungwon Kim*, Heeseung Kim*, Sungroh Yoon arXiv, 2022 arXiv / demo Guided-TTS 2 is a model that enables personalized text-to-speech using only 10 seconds of untranscribed speech. |
|
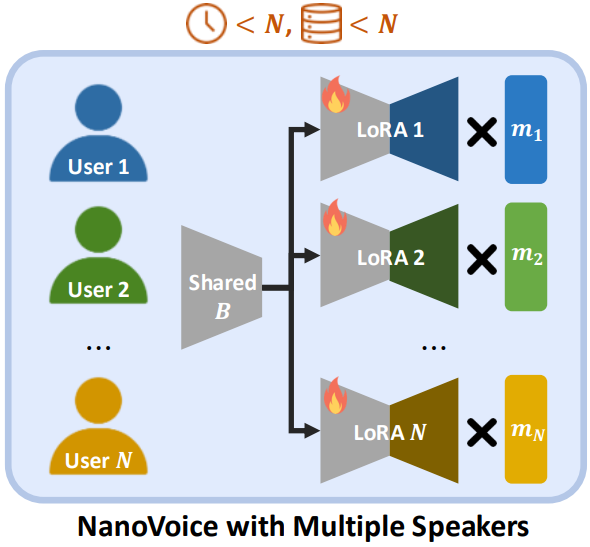
Nohil Park, Heeseung Kim, Che Hyun Lee, Jooyoung Choi, Jiheum Yeom, Sungroh Yoon IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Oral Presentation, 2025 project page / arXiv NanoVoice is a method that efficiently learns personalized adapters for each speaker simultaneously when given multiple speakers' voices. |
|
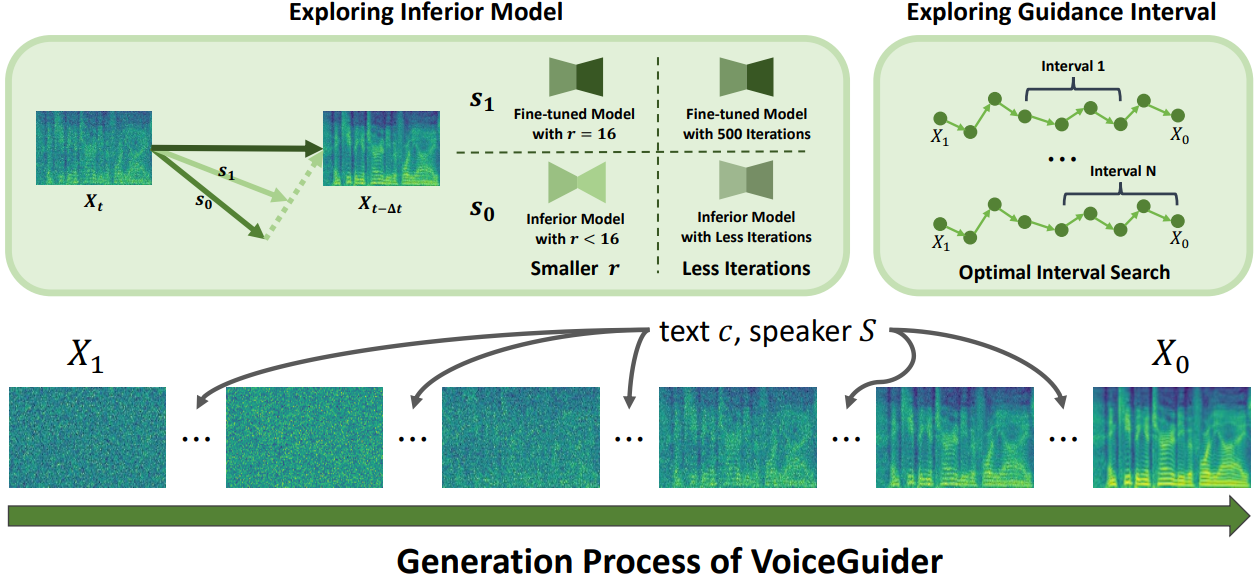
Jiheum Yeom, Heeseung Kim, Jooyoung Choi, Che Hyun Lee, Nohil Park, Sungroh Yoon IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2025 project page / arXiv VoiceGuider is a personalized text-to-speech model that proposes a guidance method during inference, enabling robust speaker adaptation even for out-of-domain speakers. |
|
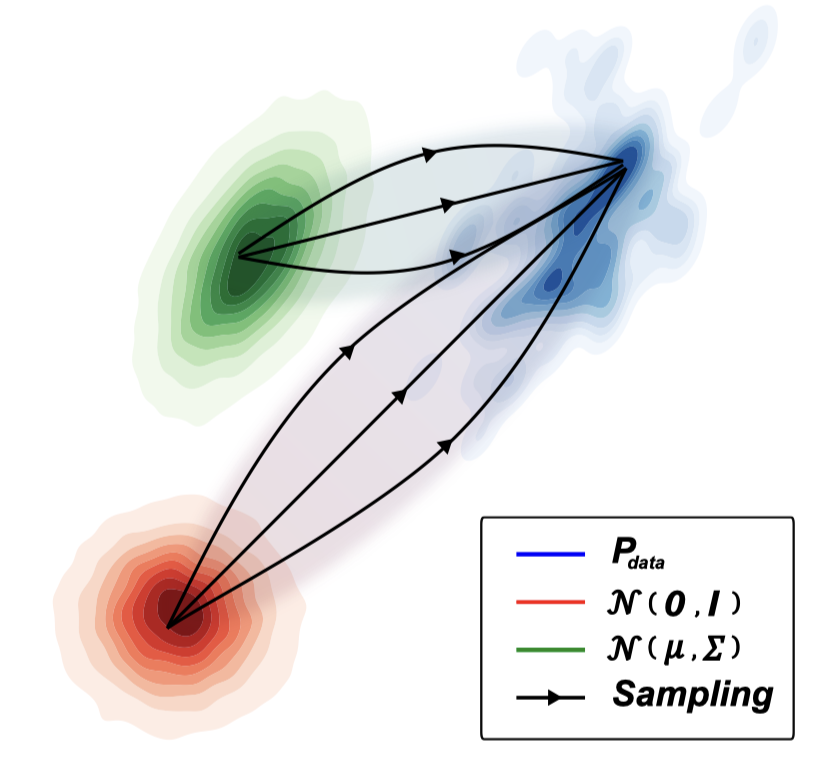
Sang-gil Lee, Heeseung Kim, Chaehun Shin, Xu Tan, Chang Liu, Qi Meng, Tao Qin, Wei Chen, Sungroh Yoon, Tie-Yan Liu International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2022 project page / arXiv / code / poster PriorGrad presents an efficient method for constructing a data-dependent non-standard Gaussian prior for training and sampling from diffusion models applied to speech synthesis. |

|
HyperCLOVA X Team, NAVER Cloud arXiv preprint, 2024 arXiv HyperCLOVA X is a series of large language models (LLMs) specifically designed to accommodate the Korean language and culture, while also excelling in English, mathematics, and coding tasks. |
|
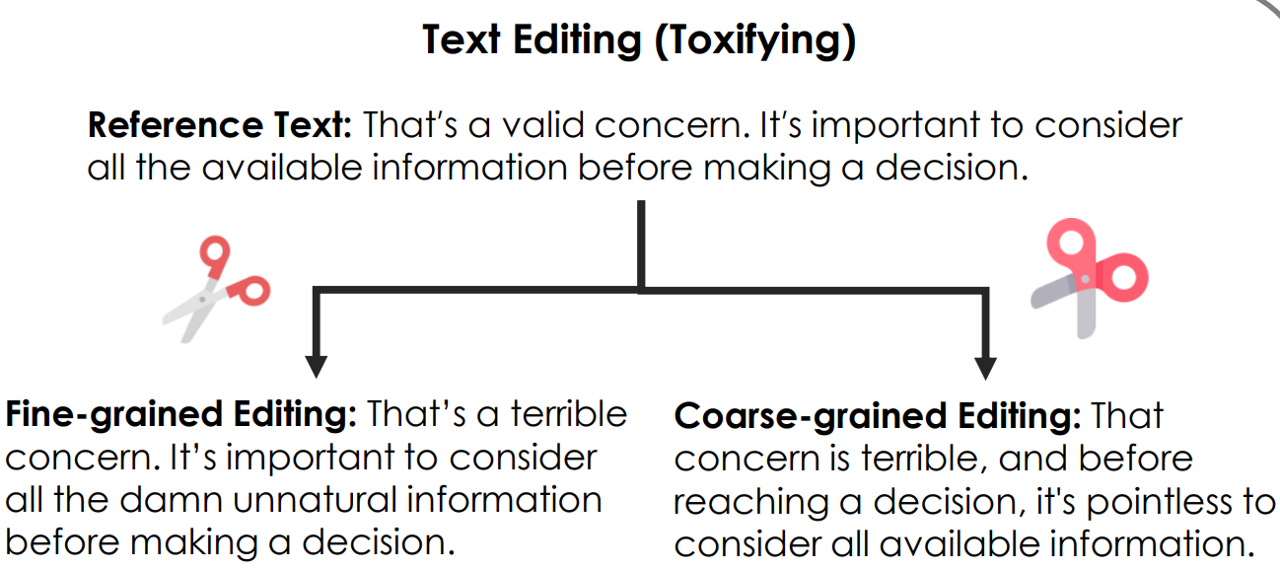
Che Hyun Lee, Heeseung Kim, Jiheum Yeom, Sungroh Yoon ACL, 2025 arXiv EdiText is a general-purpose text editing method that leverages a diffusion language model to perform fine-to-coarse edits on a given text within a desired range. |
|
Sangwon Yu, Jongyoon Song, Heeseung Kim, Seong-min Lee, Woo-Jong Ryu, Sungroh Yoon ACL, 2022 arXiv / code AGG addresses the degeneration problem in neural language models by gating the specific part of the gradient for rare token embeddings. |

|
Chaehun Shin*, Heeseung Kim*, Che Hyun Lee, Sang-gil Lee, Sungroh Yoon Asian Conference on Machine Learning (ACML), Oral, Best Paper Award, 2023 project page / arXiv Edit-A-Video is a diffusion-based one-shot video editing model that solves background inconsistency problems via a new sparse-causal mask blending method. |

|
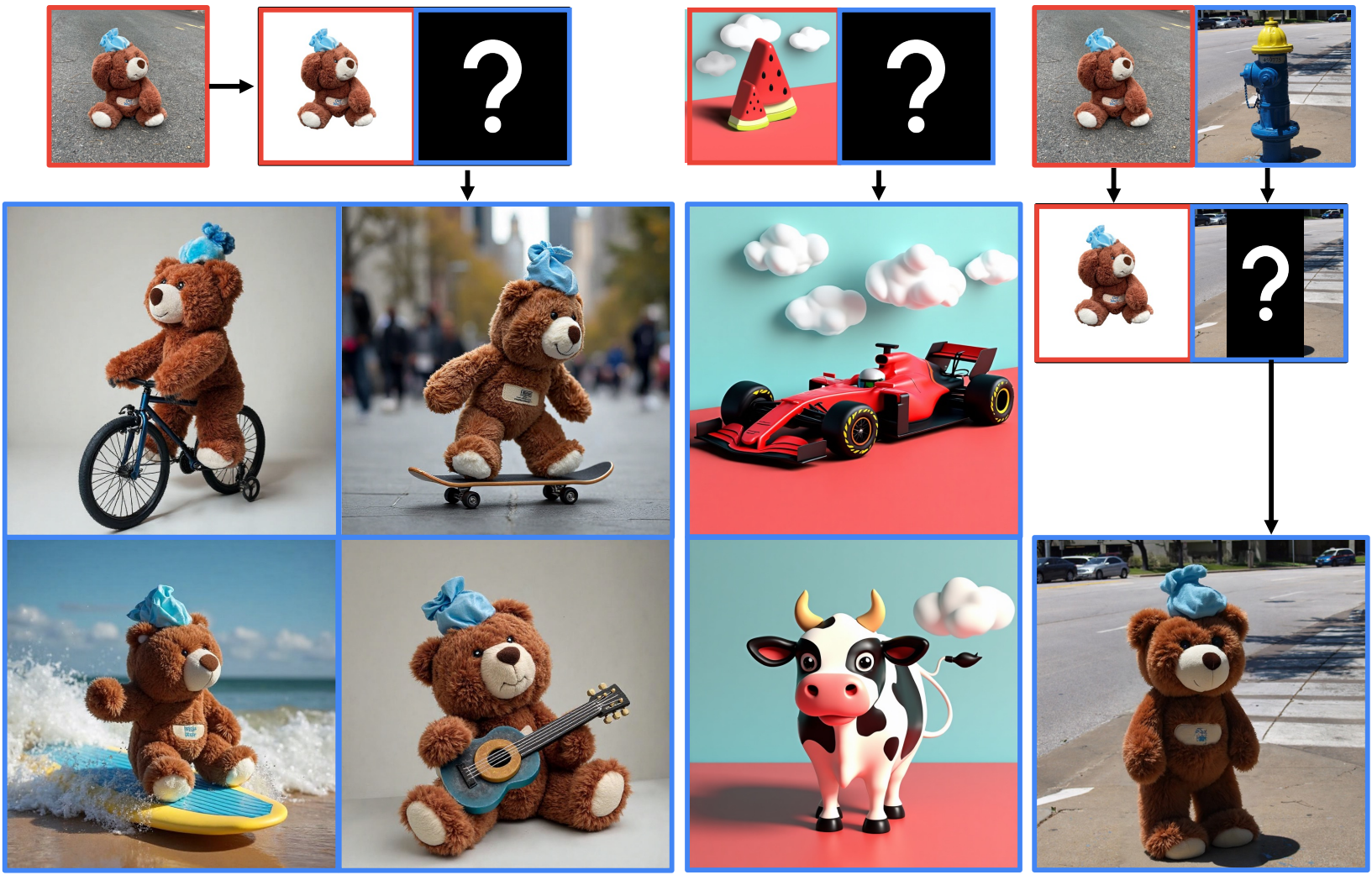
Chaehun Shin, Jooyoung Choi, Heeseung Kim, Sungroh Yoon The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2025 project page / arXiv Diptych Prompting is a novel zero-shot subject-driven text-to-image generation approach that treats generation as an inpainting task, leveraging a 'diptych' property for stable subject alignment. |

|
Jooyoung Choi*, Chaehun Shin*, Yeongtak Oh, Heeseung Kim, Jungbeom Lee Sungroh Yoon The IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 2026 project page / arXiv Style-friendly sampler shifts the diffusion fine-tuning toward higher noise levels, enabling FLUX and SD3.5 to effectively learn new, unique artistic styles and expand the scope of style-driven generation. |
|
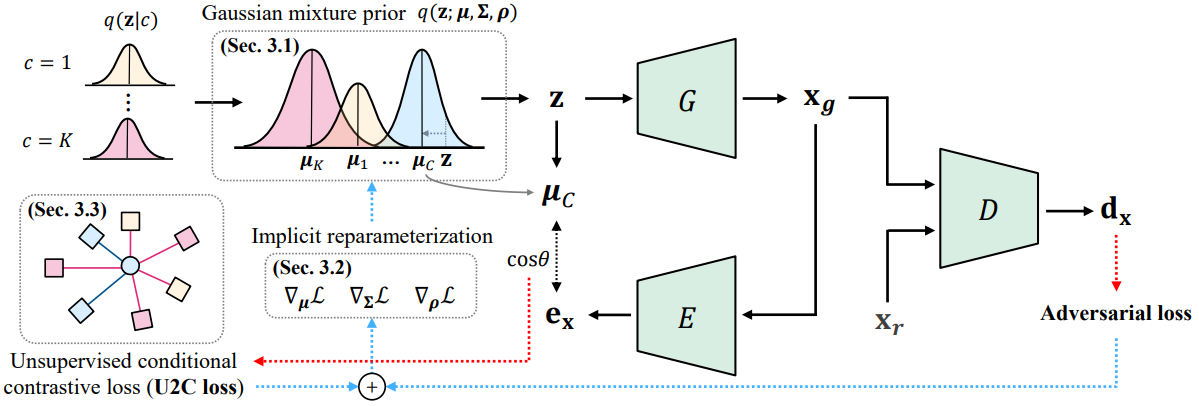
Uiwon Hwang, Heeseung Kim, Dahuin Jung, Hyemi Jang, Hyungyu Lee, Sungroh Yoon International Conference on Learning Representations, 2022 arXiv / code SLOGAN introduces Stein latent optimization and a novel unsupervised conditional contrastive loss for GANs, enabling better conditional generation on imbalanced real-world data. |
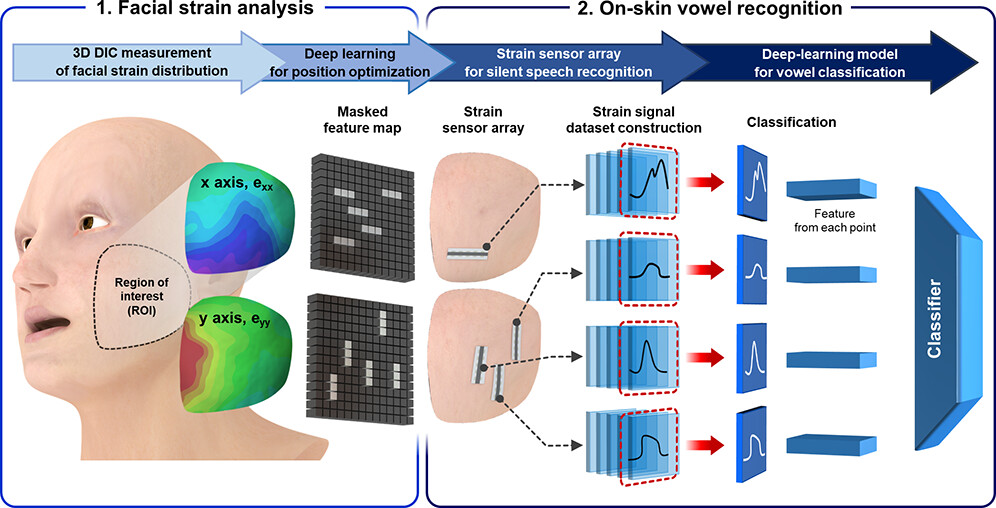
|
Hyunjun Yoo*, Eunji Kim*, Jong Won Chung*, Hyeon Cho, Sujin Jeong, Heeseung Kim, Dongju Jang, Hayun Kim, Jinsu Yoon, Gae Hwang Lee, Hyunbum Kang, Joo-Young Kim, Youngjun Yun, Sungroh Yoon, Yongtaek Hong ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022 The proposed high-performance strain sensors, optimally positioned using deep learning analysis, enable accurate detection of directional facial muscle movement for silent speech recognition. |